XYGame-AI设计3-行为树-第1版本
第一版本AI: 简单的查找目标 移动向目标 攻击目标
1.行为树:
行为树和决策树区别主要有,行为树本身除了有决策功能 还有控制行为(逻辑)功能,一种简单粗暴的方法是 通过决策树去找出解决方案,然后通过状态机去执行,
单纯的行为树除了决策功能,还要执行逻辑,也就是动作节点的执行状态 比如Running Complete 等 达到快速定位当前执行的节点在帧结束后 下一帧继续执行下去,而不用从头遍历,这涉及到 树的节点状态保存,恢复 跳转,这在设计上存在一定的难点,状态机这种有向图结构很好理解,但是变为树形结构,就比较难设计了,一种简单粗暴的方法是 通过决策树去复杂的逻辑中找出解决方案,然后通过状态机去执行,这样决策树本身就不会考虑行为之间的跳转和保留等,这样适合于行为(或者状态)本身不复杂,只是他们之间的跳转关系很复杂,
比如FPS游戏的机器人,行为很简单 就是前后左右移动 开枪,但是决策层,什么时候开枪,什么时候前走 这种就很复杂了,这种简单操作委托给状态或者目标的函数,去做,会简化设计,从而把设计本身放在设计决策层,
行为树游戏的逻辑本身主要是叶子节点(条件 行为)其余可固定至框架部分。
2.行为树代码实现分为3个部分,
BehaviorTree.cs(代码框架),Actions.cs(动作叶子节点),Conditions.cs(条件叶子节点)
3.BehaviorTree.cs框架部分:
框架版本1实现要点,每次从根节点开始遍历寻找行为并且执行,而不是
/*
* Author: caoshanshan
* Email: me@dreamyouxi.com
using Behavior Tree to peocess AI
* 行为树框架
*/
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
namespace BehaviorTree
{
//----------------行为树框架部分
/* public enum ActionNodeState
{//行为节点状态
Running,//运行中,该状态下父节点会直接运行该节点逻辑,
Looping,//循环,因为行为节点都是条件导出, 该状态会 重新 执行该层级的 比如用于持续条件评定,
Complete,//完成, 父节点可进入下个环节
// Failure,//执行失败,父节点进入下个环节
UnKnown,//默认状态,什么都不知道
}*/
public enum NodeType
{
Condition,//条件节点
Action, // 行为节点
Selector,//选择节点 从子节点选择一个执行
Sequence,//序列节点 从子节点依次执行 一般是条件 和动作的组合
Parallel,//并行节点 执行所有节点
UnKnown,
}
public class NodeBase : Model // Model for 事件系统 和 生命周期管理协议
{// 所有节点 基类
public override void OnEnter()
{
}
public override void OnExit()
{
}
public override void OnEvent(int type, object userData)
{
}
public sealed override void UpdateMS() { }
public sealed override void Update() { }
public void AddChild(NodeBase node)
{
if (IsConflict(node))
{
return;
}
node.parent = this;
children.Add(node);
}
public void RemoveChild(NodeBase node)
{
node.parent = null;
children.Remove(node);
}
public virtual bool Visit(Entity target)
{//条件节点不需要 携带参数,
return false;
}
public NodeBase parent = null;//父节点
protected ArrayList children = new ArrayList();
//----------helper function
public bool IsConflict(NodeBase other)
{// 节点间 是否冲突
// 比如 选择节点的子节点中 不应该有条件节点
return false;
}
public bool HasParent()
{
return parent != null;
}
public NodeType GetNodeType()
{
return type;
}
protected NodeType type = NodeType.UnKnown;
protected Entity _host = null;
}
public class ActionBase : NodeBase
{//行为节点基类
public ActionBase()
{
this.type = NodeType.Action;
}
}
public class ConditionBase : NodeBase
{//条件节点基类
public ConditionBase()
{
this.type = NodeType.Condition;
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------控制节点
public class ControllBase : NodeBase
{
}
public class Selector : ControllBase
{//选择节点
public Selector()
{
this.type = NodeType.Selector;
}
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{//从子节点选择一个 执行
foreach (NodeBase node in children)
{
NodeType child_type = node.GetNodeType();
if (child_type == NodeType.Condition)
{//子节点是条件节点, 条件评定
return false;// 选择节点中不应该存在 条件节点
}
else
{//选择一个节点即可
if (node.Visit(target))
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
public class Sequence : ControllBase
{//序列节点
public Sequence()
{
this.type = NodeType.Sequence;
}
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{//一个返回false 即 返回false
foreach (NodeBase node in children)
{
if (node.Visit(target) == false)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
public class Parallel : ControllBase
{//并行节点 所有节点都返回true 才返回true
public Parallel()
{
this.type = NodeType.Parallel;
}
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{//从子节点选择一个 执行 都返回false 才返回false 否则返回true
if (children.Count <= 0) return false;
bool ret = true;
foreach (NodeBase node in children)
{
if (node.Visit(target) == false)
{
ret = false;
}
}
return ret;
}
}
}
4.Actions.cs (动作节点部分)
/*
* Author: caoshanshan
* Email: me@dreamyouxi.com
Behavior Tree 's Actions
* 行为树游戏逻辑部分
*/
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
namespace BehaviorTree.Action
{
//--------------------------------------------------游戏逻辑实际的 Action
public class SearchNearestTarget : ActionBase
{//寻找最近的玩家作为目标
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{
Enemy host = target as Enemy;
if (host == null) return false;
float minDis = float.MaxValue;
Entity t = null;
foreach (Entity h in HeroMgr.ins.GetHeros())
{//找出一个最近的玩家 作为锁定目标
if (h.IsMaxTarget())
{
continue;
}
float dis = h.ClaculateDistance(host.x, host.y);
if (dis < minDis)
{
t = h;
minDis = dis;
}
}
if (t != null)
{
host.target = t;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class MoveToTarget : ActionBase
{
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{
Enemy host = target as Enemy;
if (host == null) return false;
host.dir = (int)Utils.GetAngle(host.pos, host.target.pos);//委托给Run状态去做
return true;
}
}
public class AttackTarget : ActionBase
{
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{
target.atk = true;
return true;
}
}
5. Conditions.cs (条件部分)
/*
* Author: caoshanshan
* Email: me@dreamyouxi.com
Behavior Tree 's Conditions
* 行为树游戏逻辑部分
*/
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
namespace BehaviorTree.Condition
{
//--------------------------------------------------游戏逻辑实际的 Condition
public class TargetHasNotInAtkRange : ConditionBase
{//目标不在否在攻击范围内
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{
Enemy host = target as Enemy;
if (host == null) return false;
if (host.target == null) return false;
if (host.atk_range > host.target.ClaculateDistance(host))
{//范围内
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
public class IsCDMax : ConditionBase
{//CD是否结束
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{
Enemy host = target as Enemy;
if (host == null) return false;
if (host.target == null) return false;
if (host.cd.IsMax())
{
host.cd.Reset();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class NotTargetOrDie : ConditionBase
{//没有目标或者死亡
public override bool Visit(Entity target)
{
Enemy host = target as Enemy;
if (host == null) return true;
if (host.target == null) return true;
if (host.target.isDie) return true;
return false;
}
}
}
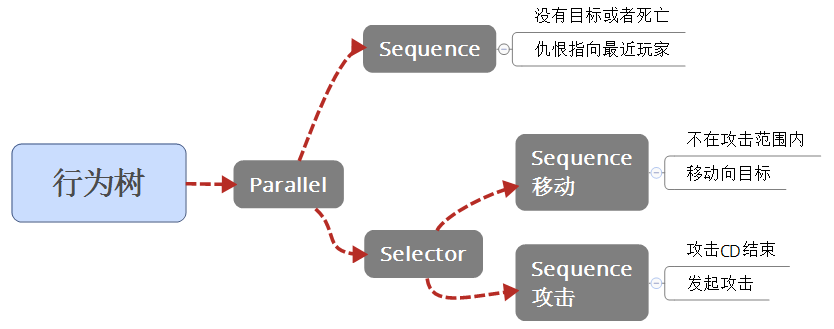
6.接入Enemy.cs,暂时手动输入树结构
private void InitBehaviorTree()
{
bt_root = new BehaviorTree.Parallel();
{
var bt_target = new BehaviorTree.Sequence();
bt_target.AddChild(new BehaviorTree.Condition.NotTargetOrDie());
bt_target.AddChild(new BehaviorTree.Action.SearchNearestTarget());
bt_root.AddChild(bt_target);
}
{
var bt_selector = new BehaviorTree.Selector();
var bt_sequence1 = new BehaviorTree.Sequence();
var bt_sequence2 = new BehaviorTree.Sequence();
bt_selector.AddChild(bt_sequence1);
bt_selector.AddChild(bt_sequence2);
bt_sequence1.AddChild(new BehaviorTree.Condition.TargetHasNotInAtkRange());
bt_sequence1.AddChild(new BehaviorTree.Action.MoveToTarget());
bt_sequence2.AddChild(new BehaviorTree.Condition.IsCDMax());
bt_sequence2.AddChild(new BehaviorTree.Action.AttackTarget());
bt_root.AddChild(bt_selector);
}
}
public virtual void AI_UpdateMSWithAI()
{
bt_root.Visit(this);
}
接入的时候 简单粗暴地每次从根节点开始遍历,
下篇 对AI本身复杂度进行丰富