曲线间平滑计算方法和一个Spline的实现
Unity曲线编辑器和bezier曲线插值—–该篇是对上篇的曲线间平滑过渡问题的展开。
上面的曲线间平滑多度强烈依赖于2条二阶曲线粘合处的平滑。
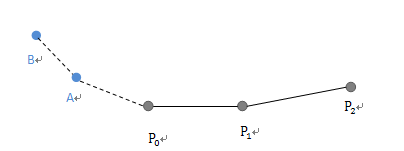
1.5点线性平滑处理,大致思想是通过历史点信息 通过线性预测方法得出插值的点,该方法如果不加以校正的话,会蝴蝶效应,例如依据的点是越来越偏离真实点。图中 A B就是根据历史p0 p1 p2 一定方法(一般可以是曲率做为参考依据)计算出来
2.利用三阶bezier曲线的,一个三点一线特性,大致是第一条曲线的第二个控制点和第一条曲线的终点和第二条曲线的第一个控制点,三点在一条线上的话,连接处就是平滑的,但是在实践的时候发现1个问题,虽然连接处平滑了,但是曲线 的曲率变化可能会偏差很大,导致过渡后曲率偏离过大, 也会导致抖动问题,看起来像是拐角突然变大or小。也依赖于拖动曲线的时候的让曲线间曲率变化不大。
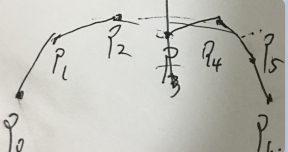
如图p2 p3 p4 在同一条线上。这个特性在editor时候可以做自动微调计算,让他们在同一个线段上
3.一片论文提到的方法 http://www.ixueshu.com/document/720e4fbfdf8eec55318947a18e7f9386.html
4.之所以不平滑是因为他们交合处角度,位置的偏差导致,平滑计算可以针对角度和位置分别进行插值处理
5.RungeKutta 算法 可用在mspline 等曲线计算中,解决步长带来的精度的问题
6.欧拉渐进法euler,也可以实现和5一样的效果,是一阶的 RungeKutta 算法
(https://www.zhihu.com/question/34780726 赵恒的回答)
————————————————————————
M-Spline方法 的一个实现, 这种方法和bezier方法区别是,这种方法生成的曲线是过控制点的,并且每个点会影响全局生成的曲线信息,因此各自的适用情况不一样。而且比例是0-1全局的,因此一个完整的曲线不适用于过大的曲线描述,受限于float精度。。
Unity曲线编辑器和bezier曲线插值—–该篇是对上篇的曲线间平滑过渡问题的展开。
上面的曲线间平滑多度强烈依赖于2条二阶曲线粘合处的平滑。
1.5点线性平滑处理,大致思想是通过历史点信息 通过线性预测方法得出插值的点,该方法如果不加以校正的话,会蝴蝶效应,例如依据的点是越来越偏离真实点。图中 A B就是根据历史p0 p1 p2 一定方法(一般可以是曲率做为参考依据)计算出来

2.利用三阶bezier曲线的,一个三点一线特性,大致是第一条曲线的第二个控制点和第一条曲线的终点和第二条曲线的第一个控制点,三点在一条线上的话,连接处就是平滑的,但是在实践的时候发现1个问题,虽然连接处平滑了,但是曲线 的曲率变化可能会偏差很大,导致过渡后曲率偏离过大, 也会导致抖动问题,看起来像是拐角突然变大or小。也依赖于拖动曲线的时候的让曲线间曲率变化不大。

如图p2 p3 p4 在同一条线上。这个特性在editor时候可以做自动微调计算,让他们在同一个线段上
3.一片论文提到的方法 http://www.ixueshu.com/document/720e4fbfdf8eec55318947a18e7f9386.html
4.之所以不平滑是因为他们交合处角度,位置的偏差导致,平滑计算可以针对角度和位置分别进行插值处理
5.RungeKutta 算法 可用在mspline 等曲线计算中,解决步长带来的精度的问题
6.欧拉渐进法euler,也可以实现和5一样的效果,是一阶的 RungeKutta 算法
(https://www.zhihu.com/question/34780726 赵恒的回答)
————————————————————————
M-Spline方法 的一个实现, 这种方法和bezier方法区别是,这种方法生成的曲线是过控制点的,并且每个点会影响全局生成的曲线信息,因此各自的适用情况不一样。而且比例是0-1全局的,因此一个完整的曲线不适用于过大的曲线描述,受限于float精度。。
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class MSplineScript : MonoBehaviour
{
public static MSplineScript ins = null;
protected Vector3[] dtbl;
protected Vector3[] ftbl;
public bool isMaked;
private float length_;
protected int lengthDiv = 8;
public Vector3[] posTbl;
protected float[] sectionLength;
protected Method useMethod = Method.ImprovedEuler;
void Awake()
{
ins = this;
}
ArrayList mpoints = new ArrayList();
void Start()
{
ins = this;
var ps = this.GetComponentsInChildren<Transform>();
var vs = new Vector3[ps.Length];
int i = 0;
foreach (var p in ps)
{
vs[i] = p.position;
++i;
}
this.Make(vs);
mpoints.Clear();
var pp = this.GetComponentsInChildren<MPont>();
foreach (var p in pp)
{
for (float iter = 0f; iter < 1f; iter += 0.001f)
{
if (Vector3.Distance(this.GetPoint(iter), p.transform.position) < 1f)
// 注意这个1f的距离取决于 曲线的精度,如果曲线很长,那么这个1可能不够
{
p.rate = iter;
break;
}
}
mpoints.Add(p);
}
}
public BezierDirection GetDirection(float rate)
{
for (int i = mpoints.Count - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
var p = mpoints[i] as MPont;
if (rate >= p.rate)
{
return p.direction;
}
}
return BezierDirection.None;
}
protected float CalcSectionLength(int section)
{
Vector3 slope;
float num2;
float num3;
int num = section;
float num6 = 1f / ((float)this.lengthDiv);
float num7 = 0f;
switch (this.useMethod)
{
case Method.Euler:
for (int i = 0; i <= this.lengthDiv; i++)
{
float rate = i * num6;
slope = this.GetSlope(num, rate);
slope.Scale(slope);
num2 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z);
num7 += num6 * num2;
}
return num7;
case Method.ImprovedEuler:
for (int j = 0; j <= (this.lengthDiv - 1); j++)
{
float num9 = j * num6;
slope = this.GetSlope(num, num9);
slope.Scale(slope);
num2 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z);
slope = this.GetSlope(num, (j + 1) * num6);
slope.Scale(slope);
num3 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z);
num7 += (num6 * (num2 + num3)) * 0.5f;
}
return num7;
case Method.RungeKutta:
for (int k = 0; k <= this.lengthDiv; k++)
{
float num11 = k * num6;
slope = this.GetSlope(num, num11);
slope.Scale(slope);
num2 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z) * num6;
slope = this.GetSlope(num, num11 + (0.5f * num2));
slope.Scale(slope);
num3 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z) * num6;
slope = this.GetSlope(num, num11 + (0.5f * num3));
slope.Scale(slope);
float num4 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z) * num6;
slope = this.GetSlope(num, num11 + num4);
slope.Scale(slope);
float num5 = Mathf.Sqrt((slope.x + slope.y) + slope.z) * num6;
num7 += ((num2 + (2f * (num3 + num4))) + num5) / 6f;
}
return num7;
}
return num7;
}
public void GetAllRateToSectionRate(float rate, out int section, out float sectionRate)
{
rate = Mathf.Clamp(rate, 0f, 1f);
section = 0;
sectionRate = 0f;
if (rate <= 0f)
{
section = 0;
sectionRate = 0f;
}
else if (rate >= 1f)
{
section = this.posTbl.Length - 1;
sectionRate = 0f;
}
else
{
float length = this.Length;
float num2 = rate * length;
float num3 = 0f;
if (this.posTbl != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.posTbl.Length; i++)
{
float sectionLength = this.GetSectionLength(i);
if ((num3 + sectionLength) > num2)
{
section = i;
float num6 = num2 - num3;
sectionRate = num6 / sectionLength;
break;
}
num3 += sectionLength;
}
}
}
}
public Vector3 GetPoint(float rate)
{
int num;
float num2;
this.GetAllRateToSectionRate(rate, out num, out num2);
return this.GetPoint(num, num2);
}
public Vector3 GetPoint(int section, float rate)
{
if (!this.isMaked)
{
return Vector3.zero;
}
if (section >= this.posTbl.Length)
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
}
if (this.ftbl == null)
{
return Vector3.zero;
}
if (this.ftbl.Length == 0)
{
return Vector3.zero;
}
int index = section;
Vector3 scale = new Vector3(rate, rate, rate);
Vector3 vector = this.ftbl[index + 1] - this.ftbl[index];
vector.Scale(scale);
Vector3 vector2 = Vector3.Scale(this.ftbl[index], new Vector3(3f, 3f, 3f));
vector += vector2;
vector.Scale(scale);
vector += this.dtbl[index + 1];
vector2 = Vector3.Scale(this.ftbl[index], new Vector3(2f, 2f, 2f));
vector -= vector2;
vector -= this.ftbl[index + 1];
vector.Scale(scale);
return (vector + this.posTbl[index]);
}
public int GetSection(float rate)
{
int num;
float num2;
this.GetAllRateToSectionRate(rate, out num, out num2);
return num;
}
public float GetSectionLength(int section)
{
if ((this.sectionLength != null) && ((section < this.sectionLength.Length) && (this.sectionLength != null)))
{
return this.sectionLength[section];
}
return 0f;
}
public float GetSectionRate(int section)
{
if ((section >= 0) && (section < (this.posTbl.Length - 1)))
{
return (this.GetSectionLength(section) / this.Length);
}
return 0f;
}
public float GetSectionRateToAllRate(int section, float rate)
{
if (section < 0)
{
return 0f;
}
if (section > (this.posTbl.Length - 1))
{
return 1f;
}
float num = 0f;
for (int i = 0; i < this.posTbl.Length; i++)
{
if (i < section)
{
num += this.GetSectionRate(i);
}
else
{
return (num + (this.GetSectionRate(i) * rate));
}
}
return num;
}
public Vector3 GetSlope(float rate)
{
int num;
float num2;
this.GetAllRateToSectionRate(rate, out num, out num2);
return this.GetSlope(num, num2);
}
public Vector3 GetSlope(int section, float rate)
{
if (section >= this.posTbl.Length)
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
}
if (this.ftbl == null)
{
return Vector3.zero;
}
if (this.ftbl.Length == 0)
{
return Vector3.zero;
}
int index = section;
Vector3 a = new Vector3(rate, rate, rate);
Vector3 vector = this.ftbl[index + 1] - this.ftbl[index];
vector.Scale(Vector3.Scale(a, new Vector3(3f, 3f, 3f)));
Vector3 vector2 = Vector3.Scale(this.ftbl[index], new Vector3(6f, 6f, 6f));
vector += vector2;
vector.Scale(a);
vector += this.dtbl[index + 1];
vector2 = Vector3.Scale(this.ftbl[index], new Vector3(2f, 2f, 2f));
vector -= vector2;
return (vector - this.ftbl[index + 1]);
}
public void Make(Vector3[] points)
{
int num2;
this.posTbl = new Vector3[points.Length];
points.CopyTo(this.posTbl, 0);
Vector3[] vectorArray = new Vector3[points.Length];
this.dtbl = new Vector3[2 * points.Length];
this.ftbl = new Vector3[2 * points.Length];
int length = points.Length;
Vector3[] vectorArray2 = vectorArray;
Vector3[] dtbl = this.dtbl;
Vector3[] ftbl = this.ftbl;
ftbl[0].x = ftbl[length - 1].x = ftbl[0].y = ftbl[length - 1].y = ftbl[0].z = ftbl[length - 1].z = 0f;
for (num2 = 0; num2 < (length - 1); num2++)
{
dtbl[num2 + 1] = this.posTbl[num2 + 1] - this.posTbl[num2];
}
ftbl[1] = dtbl[2] - dtbl[1];
vectorArray2[1].x = vectorArray2[1].y = vectorArray2[1].z = 4f;
for (num2 = 1; num2 < (length - 2); num2++)
{
Vector3 scale = new Vector3(-1f / vectorArray2[num2].x, -1f / vectorArray2[num2].y, -1f / vectorArray2[num2].z);
Vector3 vector = ftbl[num2];
vector.Scale(scale);
ftbl[num2 + 1] = dtbl[num2 + 2] - dtbl[num2 + 1];
ftbl[num2 + 1] += vector;
vectorArray2[num2 + 1] = new Vector3(4f, 4f, 4f);
vectorArray2[num2 + 1] += scale;
}
ftbl[length - 2].x -= ftbl[length - 1].x;
ftbl[length - 2].y -= ftbl[length - 1].y;
ftbl[length - 2].z -= ftbl[length - 1].z;
for (num2 = length - 2; num2 > 0; num2--)
{
ftbl[num2].x = (ftbl[num2].x - ftbl[num2 + 1].x) / vectorArray2[num2].x;
ftbl[num2].y = (ftbl[num2].y - ftbl[num2 + 1].y) / vectorArray2[num2].y;
ftbl[num2].z = (ftbl[num2].z - ftbl[num2 + 1].z) / vectorArray2[num2].z;
}
this.sectionLength = new float[this.posTbl.Length];
for (num2 = 0; num2 < this.posTbl.Length; num2++)
{
this.sectionLength[num2] = this.CalcSectionLength(num2);
}
this.isMaked = true;
this.length_ = 0f;
}
protected void GetAxisAndAngleOfPath(float rate, out Vector3 axis, out float angle)
{
Vector3 slope = GetSlope(rate);
if (slope.magnitude < 0.001f)
{
axis = Vector3.up;
angle = 0f;
}
else
{
Quaternion.LookRotation(slope).ToAngleAxis(out angle, out axis);
if (axis.y < 0f)
{
axis.Scale(new Vector3(-1f, -1f, -1f));
angle = 360f - angle;
}
}
}
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
return;
Start();
for (float t = 0f; t < 1f; t += 0.01f)
{
Debug.DrawLine(this.GetPoint(t), this.GetPoint(t + 0.01f));
}
}
public float Length
{
get
{
if (!Application.isPlaying || (this.length_ == 0f))
{
float num = 0f;
if (this.posTbl != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < (this.posTbl.Length - 1); i++)
{
num += this.GetSectionLength(i);
}
}
this.length_ = num;
}
return this.length_;
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
public float GetInvR(float nowRate)
{
Vector3 vector;
Vector3 vector2;
float num2;
float num3;
float num4 = 5f;
float rate = Mathf.Clamp01(nowRate - ((num4 * 0.5f) / Length));
float num6 = Mathf.Clamp01(nowRate + ((num4 * 0.5f) / Length));
this.GetAxisAndAngleOfPath(rate, out vector, out num2);// 直接坐标切线
this.GetAxisAndAngleOfPath(num6, out vector2, out num3);
float num7 = num3 - num2;// 当前2个点的世界坐标原点 切线的角度, 角度是基于世界坐标原点而来
if (num7 > 180f)
{
num7 -= 360f;
}
if (num7 < -180f)
{
num7 += 360f;
}
float num8 = 30f;
float num9 = 0.2f;
float num = Mathf.Atan(num7 * num9) / 1.570796f;// 角度变化量*0.2
float invR = (num * (1f / num8));
return invR;
}
[HideInInspector]
public bool CalcRate = false;
public float rate;
public void Update()
{
ins = this;
if (CalcRate == false) return;
var ps = this.GetComponentsInChildren<Transform>();
var vs = new Vector3[ps.Length];
int i = 0;
foreach (var p in ps)
{
vs[i] = p.position;
++i;
}
this.Make(vs);
GameObject.Find("CalcRate").transform.position = GetPoint(rate);
}
float nowRate = 0f;
public float IteratePathPosisionRatio(float nowRate, float sideOffset, float length)
{
float num = length / this.Length;
Vector3 point = this.GetPoint(nowRate, sideOffset);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Vector3 vector3 = this.GetPoint(nowRate + num, sideOffset) - point;
if (vector3.magnitude == 0f)
{
break;
}
float num3 = length / vector3.magnitude;
float num4 = 0.05f;
if (Mathf.Abs((float)(num3 - 1f)) <= num4)
{
break;
}
num *= ((num3 - 1f) * 0.75f) + 1f;
}
float b = nowRate + num;
return Mathf.Min(1f, b);
}
public Vector3 GetPoint(float rate, float sideOffsetRate)
{
int num;
float num2;
this.GetAllRateToSectionRate(rate, out num, out num2);
return this.GetPoint(num, num2, sideOffsetRate);
}
public Vector3 GetPoint(int section, float sectionRate, float sideOffsetRate)
{
Vector3 point;
if (sideOffsetRate == 0f)
{
point = this.GetPoint(section, sectionRate);
}
else
{
Vector3 normalized = this.GetSlope(section, sectionRate).normalized;
Vector3 vector3 = Vector3.Cross(Vector3.up, normalized);
float num = this.GetWidth(section, sectionRate, sideOffsetRate) * sideOffsetRate;
point = ((Vector3)(vector3 * num)) + this.GetPoint(section, sectionRate);
}
point.y = 0.1f;
return point;
}
public float GetWidth(float rate, float side)
{
int num;
float num2;
this.GetAllRateToSectionRate(rate, out num, out num2);
return this.GetWidth(num, num2, side);
}
public float GetWidth(int section, float rate, float side)
{
return 0.2f;
/*
float from = this.pointList[section].getWidth(side);
if (section < (this.posTbl.Length - 1))
{
from = Mathf.Lerp(from, this.pointList[section + 1].getWidth(side), rate);
}
return from;*/
}
protected enum Method
{
Euler,
ImprovedEuler,
RungeKutta
}
}
Method 表示使用何种方法进行 曲线渐进计算 欧拉法,改进的欧拉法,Rungekutta方法。。皆是上述提到的方法。